Air pollution is one of the most serious environmental and health challenges faced by Albania. With the rise of urbanization, industries, and the number of motor vehicles, pollution levels in some of the country’s major cities have reached alarming proportions. Albania is ranked fourth in Europe for air pollution levels, with a premature death rate of 164 per 100,000 people caused by exposure, according to the report “Health at a Glance” published by the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)/European Commission. 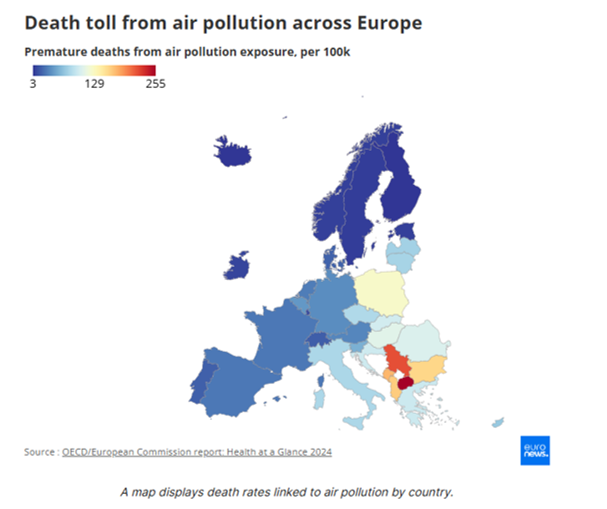
Burimi: Foto e marrë nga web faqja zyrtare e EuroNews (https://www.euronews.com/health/2025/01/11/pollution-deaths-the-air-in-these-countries-is-the-deadliest-in-europe)
The consequences of air pollution are not limited to public health but also affect biodiversity, climate, and quality of life.
In 2023, Milieukontakt Albania, in collaboration with the EPER Center, Together for Life, and GO2, under the project “Clean Air, Healthy Life” financed by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency, identified the main sources of air pollution in five major cities (Tirana, Durrës, Elbasan, Korçë, and Shkodër). Continuous monitoring of air quality parameters (CO2, NO2, PM2.5, PM10) revealed a significant gap between current air quality levels and the EU standards set out in Directive 2008/50/EC on air quality.
Main Sources of Air Pollution in Albania
- Road Transport. The increasing number of vehicles, most of which are old, is a major source of urban air pollution. Diesel-powered vehicles emit high levels of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and fine particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10).
- Industry. Industrial activities use outdated technologies, emitting pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and greenhouse gases. The lack of proper filters and enforcement of regulations contributes to increased pollution.
- Construction Activities and Illegal Burning of Waste. Construction activities and the burning of waste, including plastics and toxic materials, release harmful substances into the atmosphere. This practice is particularly common in peripheral areas.
- Wood-Burning for Heating and Seasonal Pollution. During winter, wood and coal burning for heating significantly increase air pollution levels. In coastal areas, marine vehicles used for tourism or recreation during summer contribute to air pollution.
Consequences of Air Pollution are felt on:
- Human Health. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), air pollution is a leading cause of respiratory diseases such as asthma, chronic bronchitis, and cardiovascular illnesses. In Albania, the increase in fine particulate matter (PM2.5) levels is linked to a rise in pulmonary diseases.
- Environment and Biodiversity. Air pollution damages vegetation by affecting photosynthesis and plant growth. Toxic substances emitted into the air eventually settle on land and water, negatively impacting biodiversity and natural ecosystems.
- Economic Costs. The economic costs of air pollution include healthcare expenses, reduced work productivity, and negative impacts on tourism. Polluted destinations may deter visitors, harming the tourism sector.
Steps Towards Improvement include:
- Implementation of Environmental Laws
Strengthening legislation and improving controls on emissions from construction and transport are essential. New regulations must ensure that both new and existing vehicles comply with environmental standards. - Promotion of Sustainable Transport
- Developing clean public transport systems and bicycle infrastructure can significantly reduce urban air pollution.
- Subsidizing electric vehicles and building the necessary infrastructure will encourage a shift towards more eco-friendly vehicles.
- Raising Public Awareness
Organizing educational campaigns to inform the public about the consequences of air pollution and steps they can take to reduce it is crucial. - Development of Renewable Energy
Investing in solar and wind energy can reduce dependence on fossil fuels and cut down on pollutant emissions.
Air pollution in Albania is a complex challenge that requires the cooperation of state institutions, the private sector, and citizens. Only through well-thought-out strategies and sustainable measures can public health and environmental quality be safeguarded. Every step taken towards reducing air pollution will make a difference for environment and health.
